pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
sh '''
rm -f *.html
asciidoc --backend list | grep deckjs || asciidoc --backend install deckjs-1.6.3.zip
for file in *.asciidoc
do
asciidoc $file
done
'''
}
}
stage('Tests') {
steps {
sh 'file pipeline-as-code.html'
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
}
post {
always {
archive '*.html'
echo 'I will always say Hello again!'
}
}
}Pipeline as Code
Brussels, 2017-03-30.
Fabrice Flore-Thébault
About me
Free software enthusiast
Professional life as sysadmin/devops in SME
Once upon a time co-founder of
Jeudis du Librein Brussels

Topics
Pipeline as Code conceptual overview
Jenkins Declarative Pipeline overview
To Pipeline as Code (or not) in the CI/CD landscape
Jenkins onboarding
Declarative Pipeline syntax and examples
Scripted Pipeline syntax and examples

2016 Jenkins community survey results

Pipelines color as code: learn from the metaphor
Signalisation of realworld engineering pipelines is codified.

Pipelines elements as code: learn from the metaphor
Description of realworld engineering pipelines is codified.
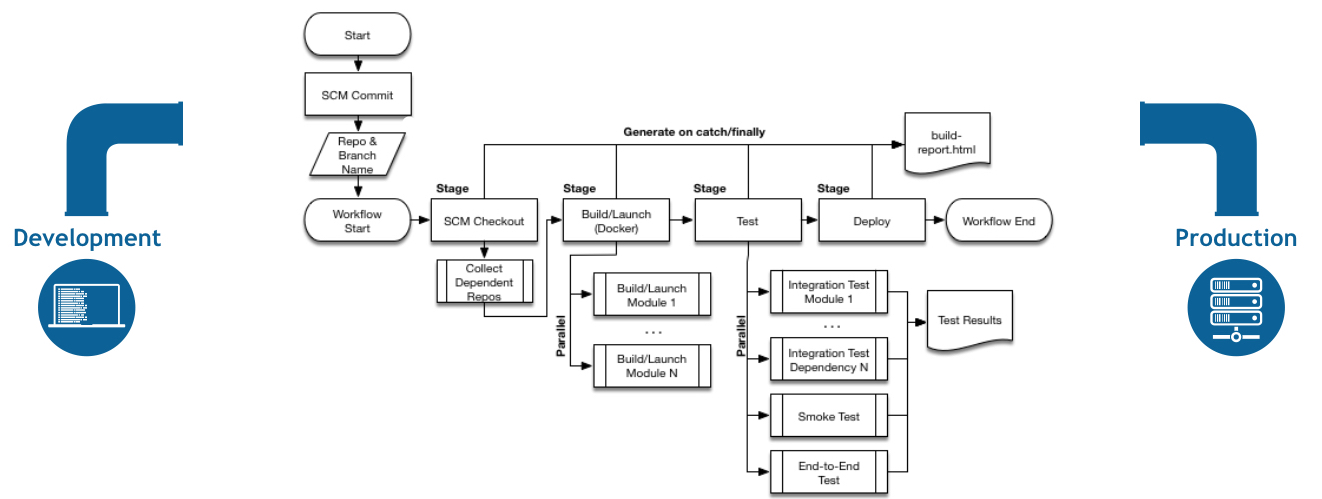
Pipeline flow concept
All that happens from Development to Production.
Downstripped metaphor is code/tools agnostic: may be performed manually, semi-automated … or transformed into code.
Full featured metaphor leads to Pipeline as Code.
* as Code: Automation is for people
Application as code
Infrastructure as code
Pipeline as code

History of (Declarative) Pipeline as code in Jenkins
2005 -
Hudson1.02011 - Forked to
JenkinsUI driven approaches: Downstream jobs, Build Pipeline View
Code driven approches: Jenkins Job Builder, Job DSL plugin
2016 -
Jenkins 2.0:PipelineandBlue Oceanplugins2017 -
Declarative Pipeline(vs. Scripted Pipeline),Pipeline Editor
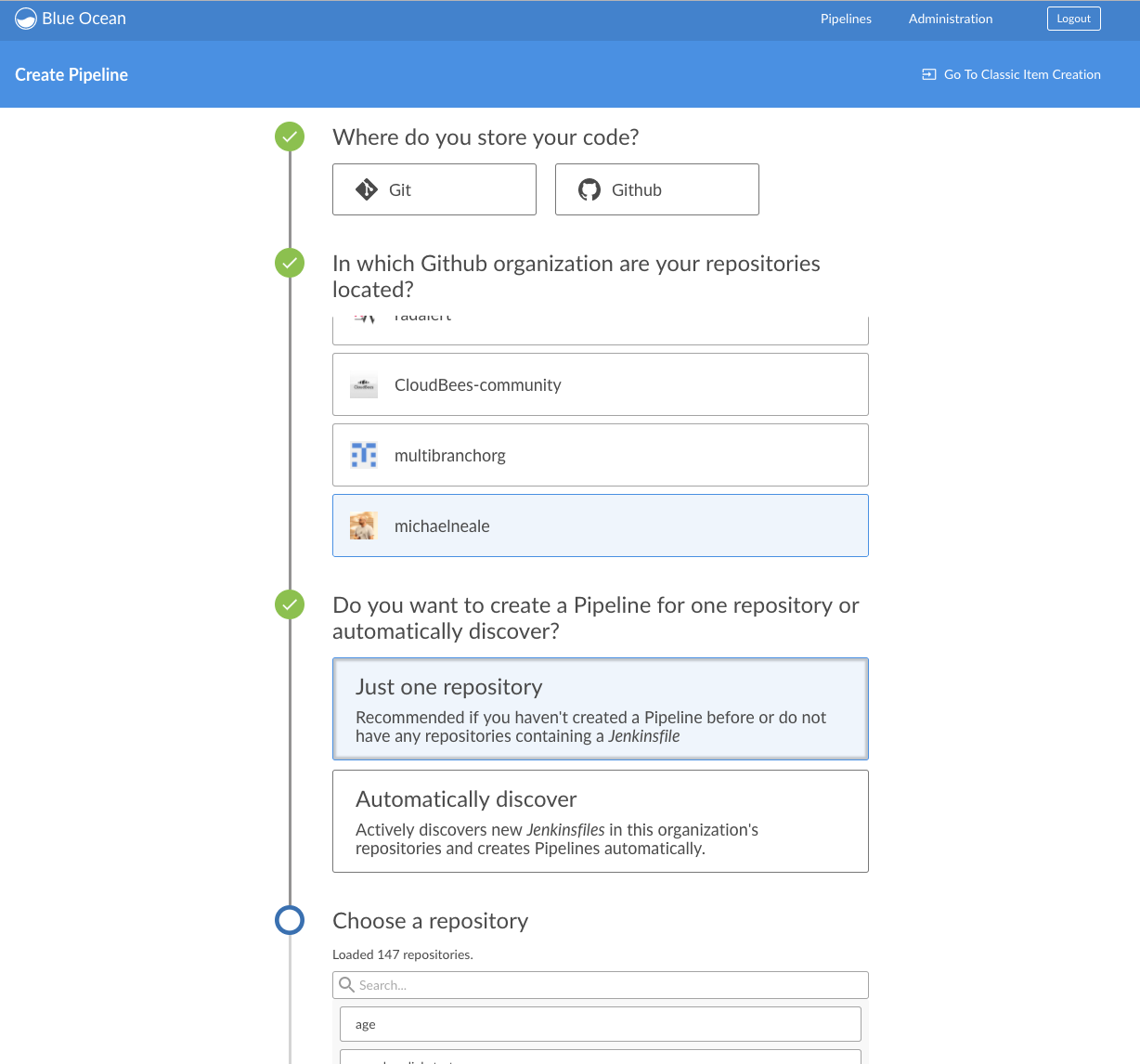
Declarative Pipeline Editor in Blue Ocean
Durability:
Jenkinsfilealways committed back to the codebase of the project.Easy: Pipeline edition for everyone!
Prerequisites: GitHub OK, other git providers like Bitbucket unsupported
Declarative Pipeline vs. Scripted Pipeline
Declarative Pipeline | Scripted Pipeline |
|---|---|
On top of | Full power of |
Consistent structure | Greater liberty |
Human readable | Complex |
Lower barrier entry | Groovy "Expert" needed |
UI Editor including syntax validation | Frequent obscure syntax errors |
Validation of syntax at the beginning of a build | Error during the build |
Error point to the point in the pipeline that is causing the problem | Difficult to find the source of error |
One step back: Pipelines in the CI/CD tools
AWS: Prescriptive
CodePipelineBitbucket, Travis: Pipeline as code (YAML)
Platform.sh:
Hooksas code (YAML)Bamboo: only the GUI
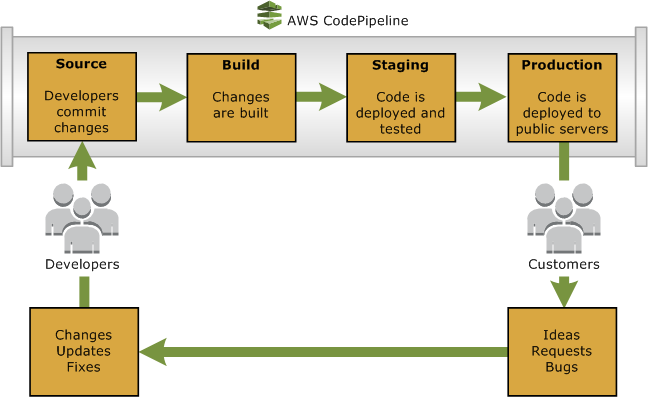
AWS CodePipeline - concept
AWS uses the Pipeline metaphor too.
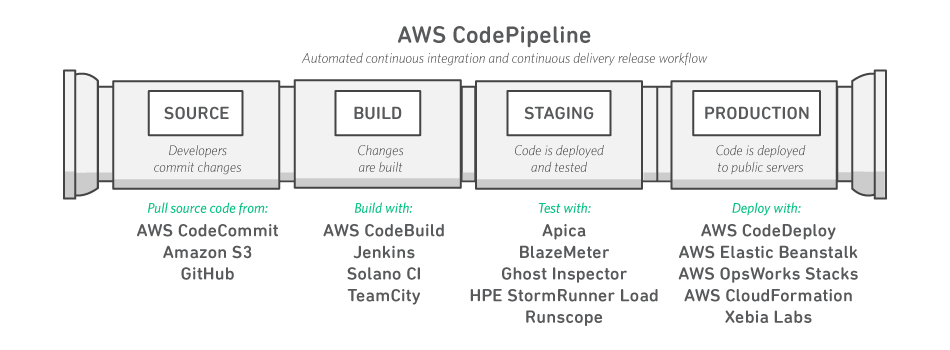
AWS CodePipeline - tools
AWS is prescriptive about compatible tools
Source cannot be on an on-premise git server (
Gitlab,Bitbucket, and so on)Jenkins is an available tool in the
Buildstage
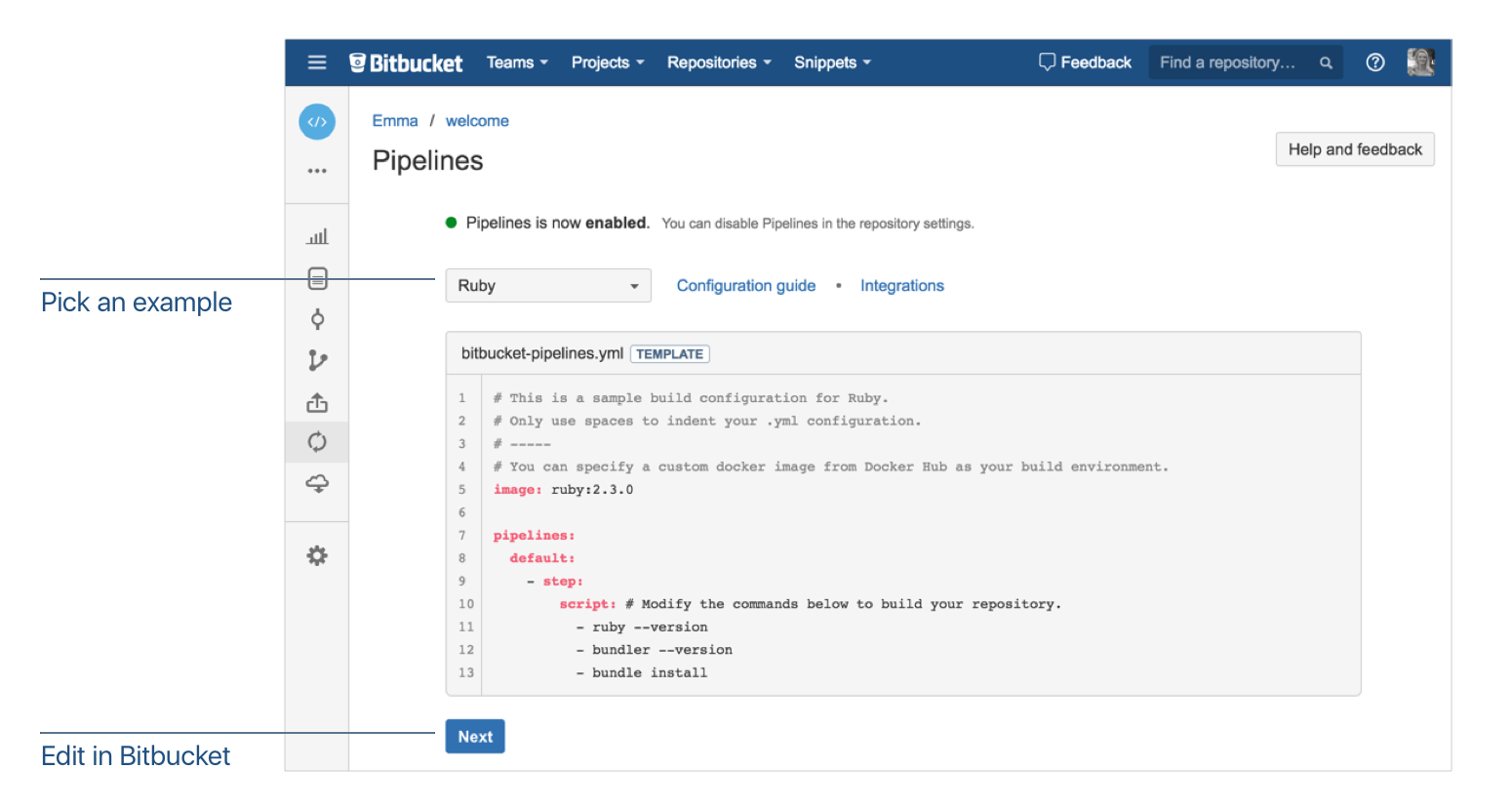
Atlassian: Bitbucket (SAAS) has Pipelines, but not Bamboo
YAML file:
bitbucket-pipelines.ymlUI proposes: Templates, raw text Editor
Bamboo, Atlassian on premise CI tool has only UI configuration, no Pipelines as Code.
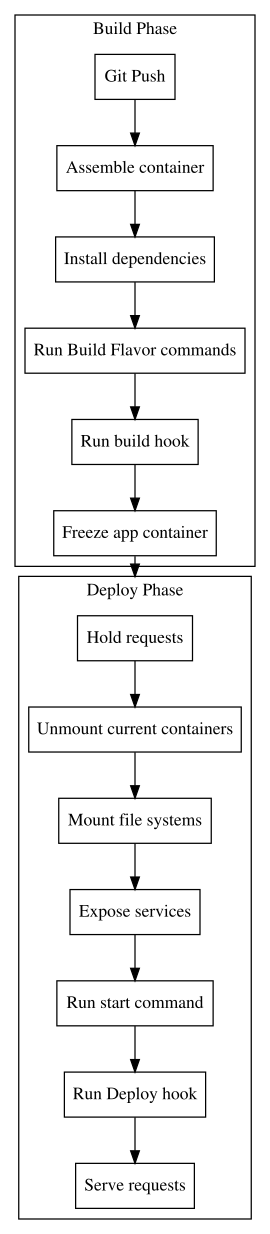
Platform.sh: build and deploy processes hooks as code
Platform.shsticks to the git vocabulary (hooks)Two fixed processes "Build" and "Deploy"
Routes, services and app as
YAMLcodeHooks are plain shell commands
LXC containers architecture
Getting started on Jenkins: Install suggested plugins
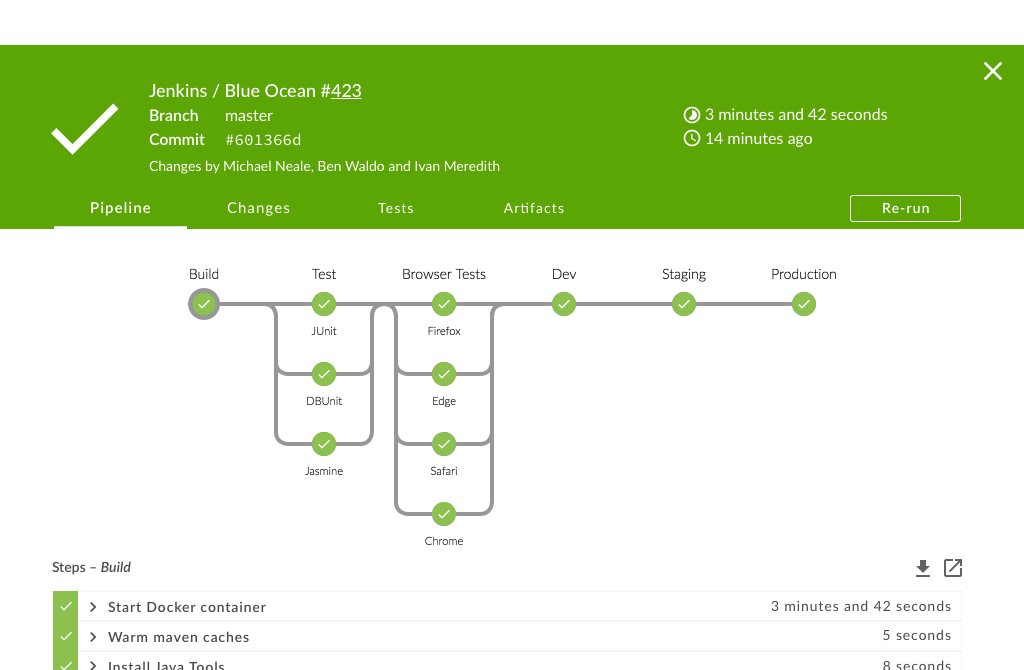
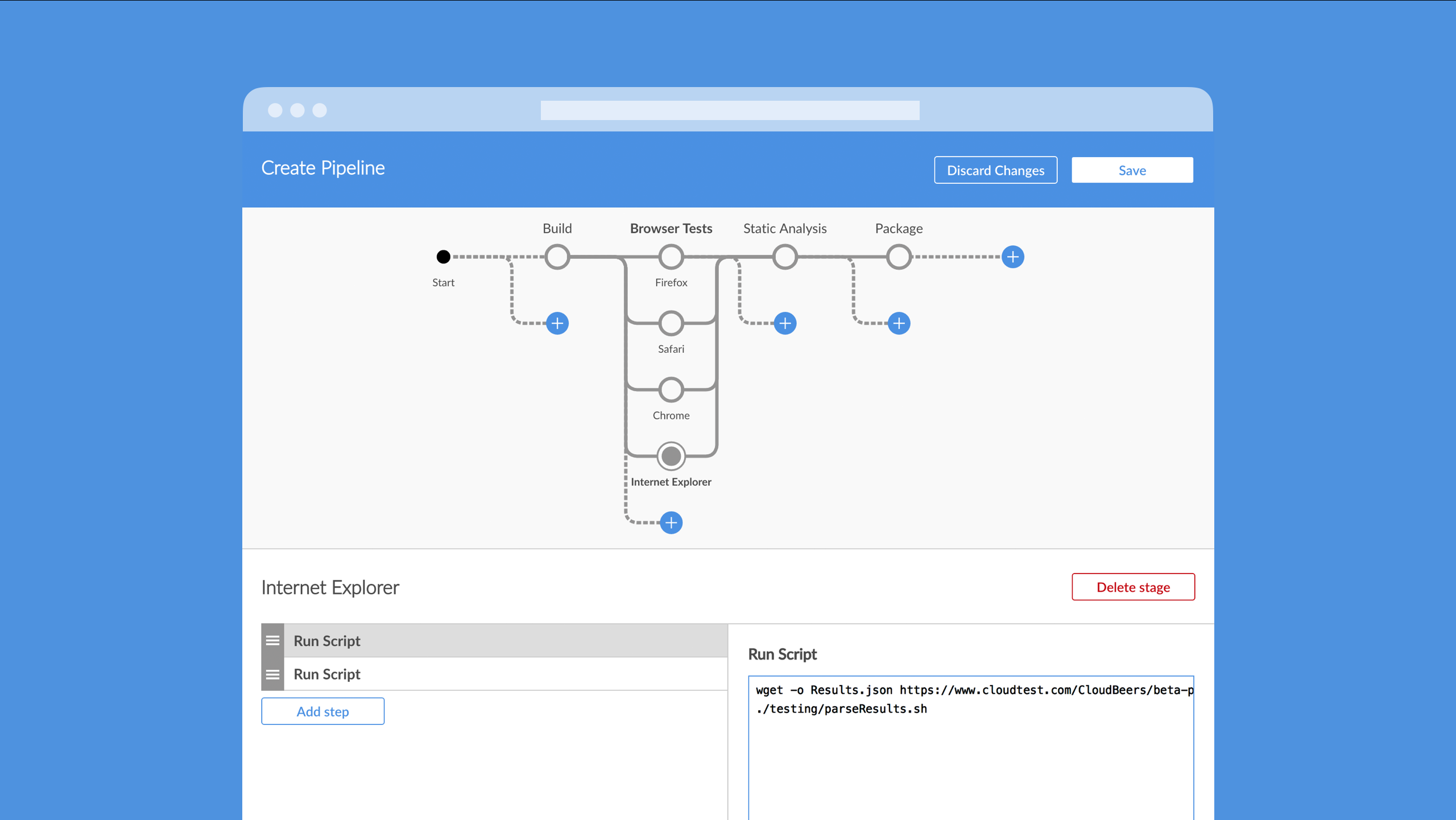
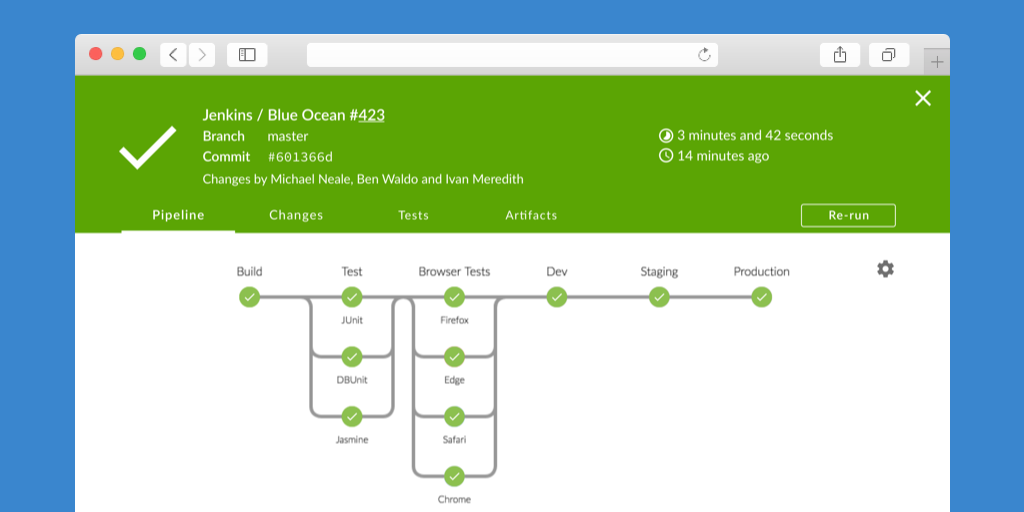
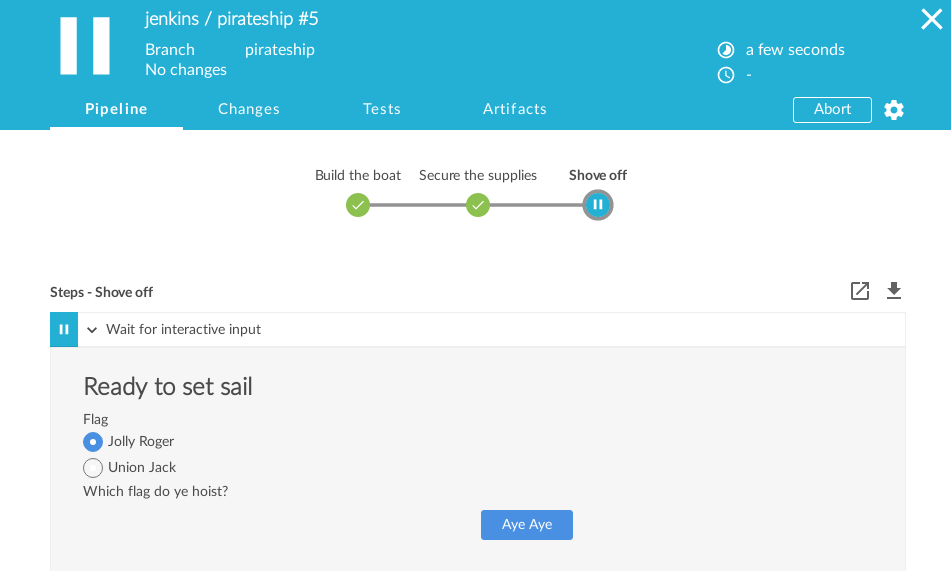
Jenkins new UI: Blue Ocean
Interactions in Blue Ocean
Jobs interactions:
Start,Abort,Re-run,InputstepConfiguration: New Pipeline, Pipeline Editor (new!)
Goodbye old interface?
Jenkins Declarative Pipeline
Improvements
A lower barrier of entry than Scripted Pipelines
Consistent structure: separate configuration from steps
Human readable
No need to be a groovy "expert"
Built for Blue Ocean visualization and UI Editor
Better error reporting
Round-tripping with the visual editor
Syntax and validation errors reported at the beginning of the build
Error point to the point in the pipeline that is causing the problem
pipeline: this makes it a declarative pipeline
pipeline {
agent {
docker "fstab/asciidoc"
}
}Environment, options and parameters
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
DISABLE_AUTH = 'true'
DB_ENGINE = 'sqlite'
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = credentials('AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID')
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = credentials('AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY')
}
options {
buildDiscarder(logrotator(numToKeepStr:'5'))
timeout(time: 30, unit: 'MINUTES')
}
parameters {
string(name: 'TARGET',
description: "Where we're deploying to",
)
}
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
sh 'printenv'
}
}
}
}stages: Running multiple steps
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
sh 'echo "Hello World"'
sh '''
echo "Multiline shell steps works too"
ls -lah
'''
}
}
}
}retry, timeout, condition
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
when {
branch "*/master"
}
retry(3) {
sh './flakey-deploy.sh'
}
timeout(time: 3, unit: 'MINUTES') {
sh './health-check.sh'
}
}
}
}
}Post: finishing up
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Test') {
steps {
sh 'echo "Fail!"; exit 1'
}
}
}
post {
always {
echo 'This will always run'
archive '*.html'
}
success {
echo 'This will run only if successful'
}
failure {
echo 'This will run only if failed'
mail to: 'team@example.com',
subject: "Failed Pipeline: ${currentBuild.fullDisplayName}",
body: "Something is wrong with ${env.BUILD_URL}"
}
unstable {
echo 'This will run only if the run was marked as unstable'
}
changed {
echo 'This will run only if the state of the Pipeline has changed'
echo 'For example, if the Pipeline was previously failing but is now successful'
}
}
}Scripted Pipeline build blocks: heavyweight vs. flightweight
// Wait outside an executor context
input "Do you want to continue?"
node('php') {
// Do something heavy
}Scripted Pipeline build blocks: try, catch, finally
try {
// do something
}
catch (e) {
// In case of failure
throw e
}
finally {
// Success or failure, always do ...
}Scripted Pipeline build blocks: cancel obsolete jobs
milestone 10
notify_build('STARTED')
build_project()
milestone 20
deploy_now('dev')
milestone 30Scripted Pipeline: define the workflow
/*
* The workflow: Gitflow.
* On branch develop, deploy automatically to development.
* On master branch, deploy automatically to QA, and wait for a validation before deploy to production.
* Obsolete builds are canceled.
* Externalize the content of the build and deploy tasks.
*/
try {
node('php') {
milestone 10
notify_build('STARTED')
build_project()
milestone 20
switch ( "${env.BRANCH_NAME}" ) {
case "develop":
milestone 30
deploy_now('dev')
milestone 40
return
case "master":
milestone 30
deploy_now('stg')
milestone 40
return
}
}
switch ( "${env.BRANCH_NAME}" ) {
case "master":
milestone 60
deploy_after_validation('prd')
milestone 80
return
}
}
catch (e) {
currentBuild.result = "FAILED"
throw e
}
finally {
// Success or failure, always send notifications
notify_build(currentBuild.result)
}Scripted Pipeline: The build step
Identified as a "stage"
Reusable: externalise project specific variants in external scripts.
Adaptable: can be fully customized for a specific project.
/*
* Define how to build a project.
* We assume we are already in a node context.
*/
def build_project() {
stage ("Build") {
// get some information about the build environment
echo "branch name: ${env.BRANCH_NAME}"
sh "env"
// Get versioned files
checkout scm
// Build -- adapt to your project
dir('www') {
sh "sh ../.jenkins/build.sh"
archiveArtifacts(
artifacts: '**',
fingerprint: true,
onlyIfSuccessful: true
)
}
}
}Scripted Pipeline: the deploy step
Reusable : Usage of variables for each environment
Adaptable: here a deployment with Ansible. Other methods are available.
Secure: credentials stored in Jenkins, the project has only a reference to the credentialsID https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/JENKINS/Credentials+Plugin
/*
* Define how to deploy a project without waiting.
* We assume we are already in a node context.
* Deployment on corresponding environment will be attempted only if the file exist in the '.jenkins/config' directory:
* - dev.groovy
* - tst.groovy
* - stg.groovy
* - prd.groovy
*/
def deploy_now(String targetEnv = 'dev') {
stage ("Deploy to ${targetEnv}") {
go = 'undefined'
try {
// load parameters for the environment ${targetEnv}
load path: ".jenkins/${targetEnv}.groovy"
echo "Variables defined for deployment in .jenkins/${targetEnv}.groovy : " +
"credentialsID=${credentialsId}, " +
"server=${target_server}, " +
"user=${target_user}"
go = 'true'
}
catch (e) {
echo "No deployment done since the environment is not defined in .jenkins/${targetEnv}.groovy"
go = 'false'
}
//echo "${go}"
if ( "${go}"== 'true' ) {
ansiblePlaybook(
credentialsId: "${credentialsId}",
extras: "--user=${target_user} --verbose",
installation: "ansible",
inventory: "${target_server},",
playbook: ".jenkins/deploy.yml",
sudoUser: null
)
}
}
}Scripted Pipeline as code: Jenkinsfile, the validation step
Wait for customer validation before deploying to production
Ensure it is the same code as the validated code that gets deployed.
Flyweight vs. heavyweight: not in a "node" context.
/*
* Define how to wait for user validation before launching a deploy.
* We assume we are outside of a node context.
*/
def deploy_after_validation(String targetEnv = 'dev') {
stage ("Validate to deploy to ${targetEnv}") {
timeout(time: 100, unit: 'DAYS') {
hipchatSend(
color: 'PURPLE',
message: "User input requested : Job '${env.JOB_NAME} [${env.BUILD_NUMBER}]' (${env.BUILD_URL})"
)
input "Deploy to ${targetEnv}?"
}
}
node('php') {
deploy_now("${targetEnv}")
}
}Some useful lectures
Jenkins documentation: https://jenkins.io/doc/
Presentation at FOSDEM 2017: https://jenkins.io/blog/2017/03/16/fosdem-event-report/
State of the jenkins automation by @roidelapluie: https://www.slideshare.net/roidelapluie/state-of-the-jenkins-automation
Challenges
What is the real laziness? How to make Pipeline as Code the least effort scenario?
Who is responsible? Who is maintaining? Not "my code" vs. "my infrastructure".
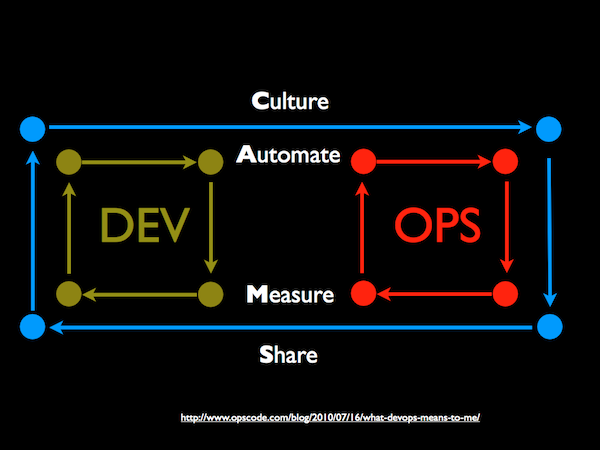
Need to educate Devops core values:
Culture
Automation
Measurement
Sharing